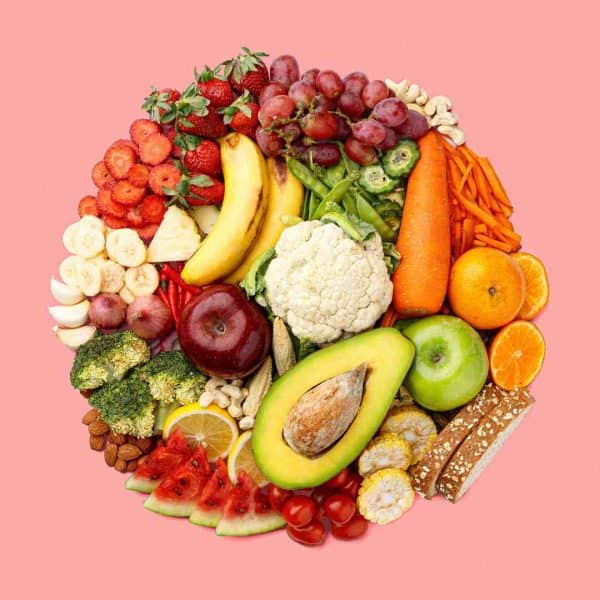

In this article, we’ll examine the results of three different studies that drew related conclusions about the impact of fruits and vegetables on your health. From mental health to cardiovascular function to lifespan, these studies found that eating more fruits and vegetables correlated with better outcomes.
Fruit and Vegetable Intake and Mortality
A study published in the journal Circulation in March 2021 found a correlation between fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of early death.
Researchers followed two cohorts of participants in large health studies and analyzed 24 other prospective cohort studies. The two cohorts included 66,719 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (1984–2014) and 42,016 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986–2014). All participants were free from cardiovascular disease (CVD), cancer, and diabetes at the start of the studies.
Participants’ diets were assessed using a validated semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire that they updated every two to four years. The researchers combined this data with findings from their review of 24 additional studies and conducted a dose-response meta-analysis to assess the correlation between fruit and vegetables servings and mortality risk.
The researchers found that about five daily servings of fruit and vegetables, or two servings of fruit and three servings of vegetables were associated with the lowest mortality. Additional servings beyond this amount were not associated with further reductions in risk.
The study also considered subgroups of fruits and vegetables, finding that most were associated with lower mortality, except for starchy vegetables such as peas and corn.
Synopsis
A large study assessed the diets and mortality outcomes of tens of thousands of participants along with data from 26 additional studies. They found that eating about five daily servings of fruit and vegetables reduced the risk of death.
Fruits, Vegetables, And Mental Health
A study published in the journal Nutrients in 2020 conducted a systematic review of 61 observational studies analyzing the association between fruit and vegetable intake and mental health in adults.
The studies they included primarily focused on depression and depressive symptoms, but also analyzed general and mental well-being, quality of life, sleep quality, life satisfaction, flourishing, mood, self-efficacy, curiosity, creativity, optimism, self-esteem, stress, nervousness, happiness, anxiety, minor psychiatric disorders, distress, and attempted suicide.
Stronger Bones. Without Drugs. Guaranteed!
The natural and evidence-based program that helps reverse osteoporosis and osteopenia in 12, 6, even 3 months… guaranteed.
The analysis indicated that high total intake of fruits and vegetables promoted higher levels of optimism and self-efficacy, reduced the level of psychological distress, and protected against depressive symptoms.
This study found that specific subgroups of fruits and vegetables were linked to these positive outcomes. Those subgroups included berries, citrus, and green leafy vegetables.
Mental health is a cornerstone of overall health and wellbeing, including bone health. Symptoms such as depression and anxiety often interfere with bone-healthy habits, making it difficult to follow bone-building strategies such as regular exercise or preparing alkalizing meals.
Synopsis
A systematic review of 61 observational studies compared fruit and vegetable intake to mental health outcomes. The study found that high total intake of fruits and vegetables promoted increased levels of optimism and self-efficacy, reduced the level of psychological distress, and protected against depressive symptoms.
Fruits And Vegetables Take On Cardiovascular Disease And Cancer
Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology published a study in the International Journal of Epidemiology that suggests that the current recommendation for fruit and vegetable intake is too low.
The researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 95 prospective studies of fruit and vegetable intake and cardiovascular disease, total cancer, and all-cause mortality.
The study found that for every 200-gram increase in consumption, participants’ risk of stroke and premature death decreased by 10.8 percent. That dose-response increase remained consistent for intakes exceeding 800 grams.
In the US, a serving of fruit or vegetables is about 125 grams, so the recommended five servings a day amounts to 625 grams. This study found significant benefits from consuming seven to eight servings per day, challenging previous findings that suggested no additional benefit beyond five daily servings.
Rates of coronary heart disease, stroke, cardiovascular disease, total cancer, and all-cause mortality each decreased with each additional 200 grams of fruits and vegetables that participants consumed. When researchers analyzed fruit and vegetable consumption separately, they found similar results for each group.
Further analysis of subgroups of fruits and vegetables also produced specific results that you can use to guide your dietary choices.
“Inverse associations were observed between the intake of apples and pears, citrus fruits, green leafy vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, and salads and cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality, and between the intake of green-yellow vegetables and cruciferous vegetables and total cancer risk.”3
The findings of all three studies align with the Save Institute’s 80/20 pH-balanced diet. Alkalizing fruits and vegetables must make up the majority of your diet to accomplish the 80/20 balance of alkalizing to acidifying foods.
While the 80/20 balance is designed to prevent acidification from weakening your bones, it also provides you with the substantial benefits observed in these studies.
Synopsis
Norwegian researchers found an association between each 200 grams of participants’ fruit and vegetable intake and a reduction in their risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and death.
What This Means To You
The studies reviewed today offer further scientific evidence that a pH-balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides benefits beyond bone strengthening. This is the power and efficiency of a holistic approach to preventing and reversing osteoporosis — the benefits of your choices aren’t limited to your bones.
The Osteoporosis Reversal Program provides you with deep knowledge and simple steps to strengthen your bones, and as you follow them, you may also notice improvements in your overall health. The ORP avoids the tunnel vision of the Medical Establishment. It doesn’t trade off one part of your health for another. Following the ORP causes no negative side effects, only overall improvements that come with stronger, more resilient bones.
Preventing fractures allows you to stay active and independent. Make sure you maintain your overall health so that you can enjoy your freedom to its fullest.
Stronger Bones. Without Drugs. Guaranteed!
The natural and evidence-based program that helps reverse osteoporosis and osteopenia in 12, 6, even 3 months… guaranteed.
References
1 https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048996








Hi there!
I do enjoy these updates .HoweverI am just wondering ..
Is there anyone who can relate their positive experience of dealing with osteoporosis without drugs ?
I was diagnosed with this condition about 4 years ago and had Prolia only once or twice .I am a very healthy eater, have been a walker for many years and now do weights ( for two years ) and other exercises eg yoga , dance and little runs here and there .
.I am a very active almost 75 year old .
I feel in despair as the scan I had last week shows a big deterioration .Particularly in my back and hips .I pride myself on being healthy and not keen on taking medication .My doctor really layed it on the line.Just wondered if anyone had anything to say that may give me heart .I feel like a wreck !
Thank you for reading my tale of woe .I am open to any thoughts , but I have had enough doom and gloom for one day
Thank you .and all the best .Bethanne
I try to eat as many vegetabels as possible, and now I’m going to add more and some fruits. Thanks for the interesting information!
That’s a good move on your part! And you’re very welcome, Ruth!
I knew that fruits and veggies are good for us, but this goes beyond. Thank you Vivian!
My pleasure, Lenny!
Thanks Vivian. More encouragement for my old bones!
I do enjoy fruit and vegetables and will endeavour to eat more of them knowing that they also help the bones. Brocolli is a great favourite.
Betty
You’re welcome, Betty! And that’s great! Broccoli is very healthy and can be easily incorporated into meals. Enjoy!